
Continuous improvement is the cornerstone of successful manufacturing operations. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of continuous improvement in manufacturing, emphasizing the role of performance management as a catalyst for progress. We will also explore the importance of implementing a feedback loop for ongoing performance evaluation, the value of employee involvement in identifying and implementing improvements, and the power of the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle as a tool for continuous enhancement.
Continuous improvement, often known as Kaizen in manufacturing, is the relentless pursuit of small but meaningful enhancements throughout the production process. It involves identifying inefficiencies, eliminating waste, and optimizing procedures to elevate productivity, quality, and customer satisfaction. Embracing continuous improvement empowers organizations to stay nimble, competitive, and adaptable in the face of market changes.
Performance management is pivotal in steering continuous improvement within manufacturing. It comprises setting clear performance goals, regular monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs), and analyzing performance data to pinpoint areas ripe for improvement. By aligning performance management with continuous improvement principles, organizations foster a culture that values data-driven decision-making, accountability, and the relentless pursuit of excellence.
A critical facet of performance management is establishing an open feedback loop for consistent performance evaluation. This entails regularly gathering and scrutinizing data to assess performance against predetermined targets and benchmarks. This feedback loop enables organizations to identify trends, spot improvement opportunities, and make timely adjustments to processes and operations. Leveraging technology and data analytics enhances the efficiency of the feedback loop, providing valuable insights to guide decision-making.
Employees are the lifeblood of any successful manufacturing operation. Encouraging their active participation in identifying and implementing improvements is indispensable for sustained growth. Cultivating a culture that values employee ideas, fosters creativity, and empowers them to contribute to continuous improvement initiatives significantly impacts organizational performance. Regularly seeking input from frontline workers, who have an intimate understanding of the processes, can lead to innovative solutions and imbue employees with a sense of ownership.
The PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle, also known as the Deming Cycle, is a robust problem-solving methodology that supports continuous improvement efforts. Let’s delve into each stage of the PDCA cycle:
The PDCA cycle offers structured problem-solving, data-driven insights, adaptability, and employee engagement. It enables organizations to make informed decisions, standardize successful practices, and continuously refine their processes.
The PDCA cycle is adaptable across various industries and organizations. It excels at exploring effects in a controlled environment, minimizing waste through small-scale testing, and identifying the most effective improvements tailored to unique needs.
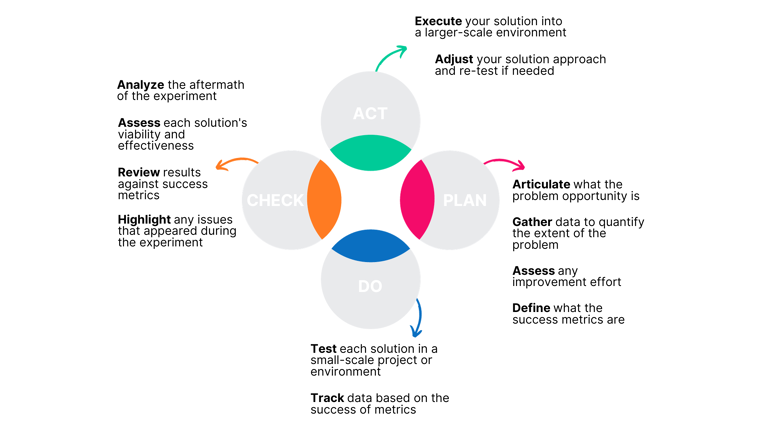
The PDCA cycle is an ongoing process that becomes ingrained in an organization’s culture, guiding consistent improvement in products, services, or processes. Continuous improvement, driven by performance management and supported by the PDCA cycle, positions manufacturing operations for excellence, efficiency, and sustained growth in a dynamic business landscape. Embrace these principles, and your organization will thrive in the ever-evolving world of manufacturing.

Standardization plays a pivotal role in enhancing operational efficiency across industries. In the manufacturing sector, data standardization is crucial for…

Imagine a factory floor bustling with activity, but not just machines in motion. Data flows seamlessly, painting a clear picture…

The manufacturing landscape is awash in data, a torrent of information flowing from diverse sources – legacy systems, cutting-edge technology,…
Get monthly updates to know how you can improve process performance and drive efficiency within your existing organisation.

